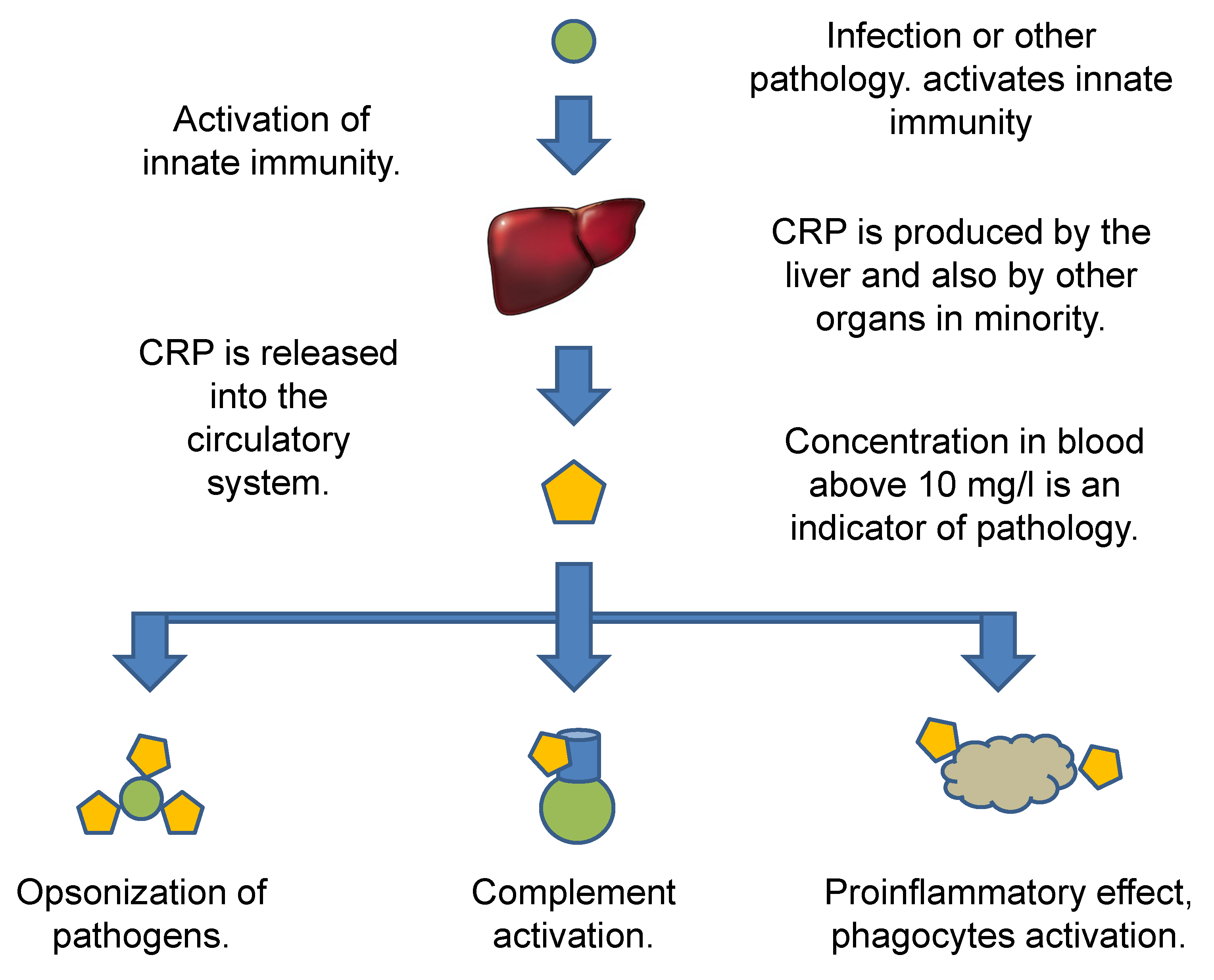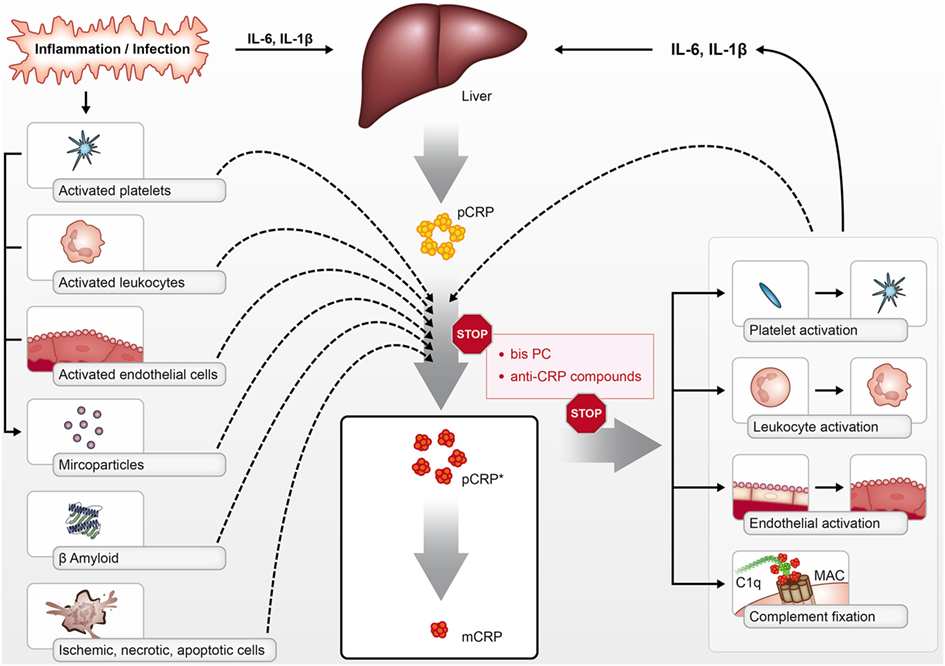
Frontiers | Dissociation of C-Reactive Protein Localizes and Amplifies Inflammation: Evidence for a Direct Biological Role of C-Reactive Protein and Its Conformational Changes

Use of multiple inflammatory marker tests in primary care: using Clinical Practice Research Datalink to evaluate accuracy | British Journal of General Practice
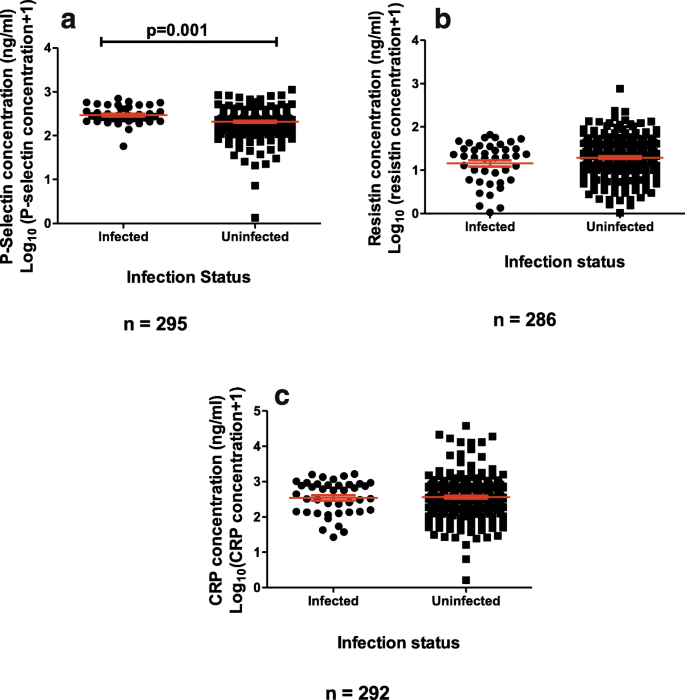
Elevation of C-reactive protein, P-selectin and Resistin as potential inflammatory biomarkers of urogenital Schistosomiasis exposure in preschool children | BMC Infectious Diseases | Full Text
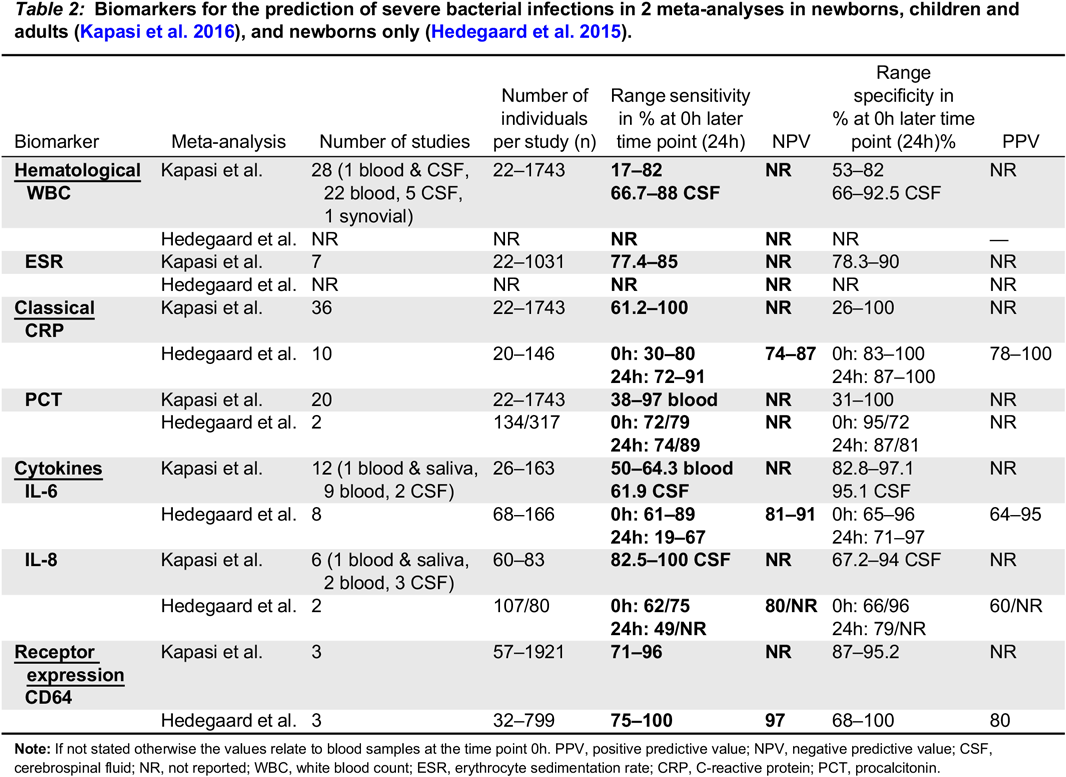
C-reactive protein and other biomarkers—the sense and non-sense of using inflammation biomarkers for the diagnosis of severe bacterial infection

C-Reactive Protein and Other Circulating Markers of Inflammation in the Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease | NEJM

Differential Markers of Bacterial and Viral Infections in Children for Point-of-Care Testing: Trends in Molecular Medicine

C-reactive protein and albumin kinetics after antibiotic therapy in community-acquired bloodstream infection - ScienceDirect
Human C-reactive protein: major non-specific marker of inflammation and predictor of future cardiovascular diseases risk. - Advanced ImmunoChemical Inc.Advanced ImmunoChemical Inc.
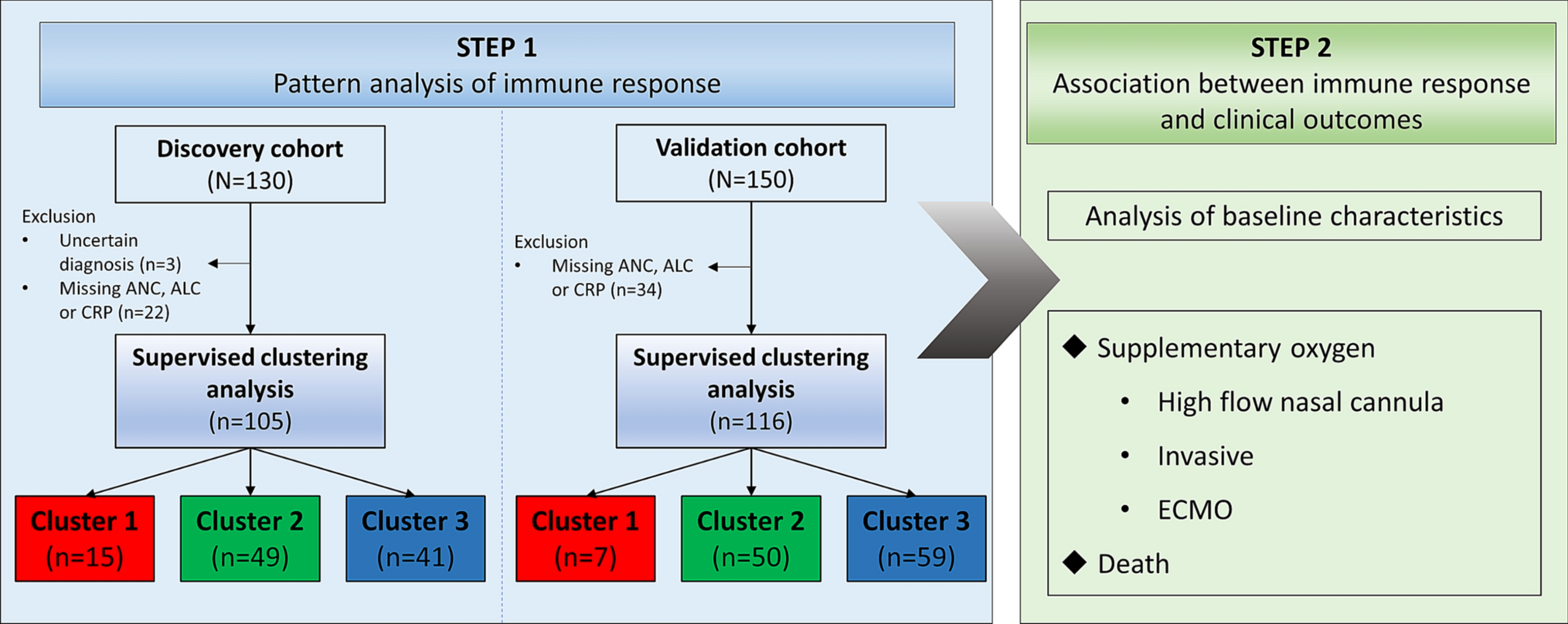
Pattern of inflammatory immune response determines the clinical course and outcome of COVID-19: unbiased clustering analysis | Scientific Reports
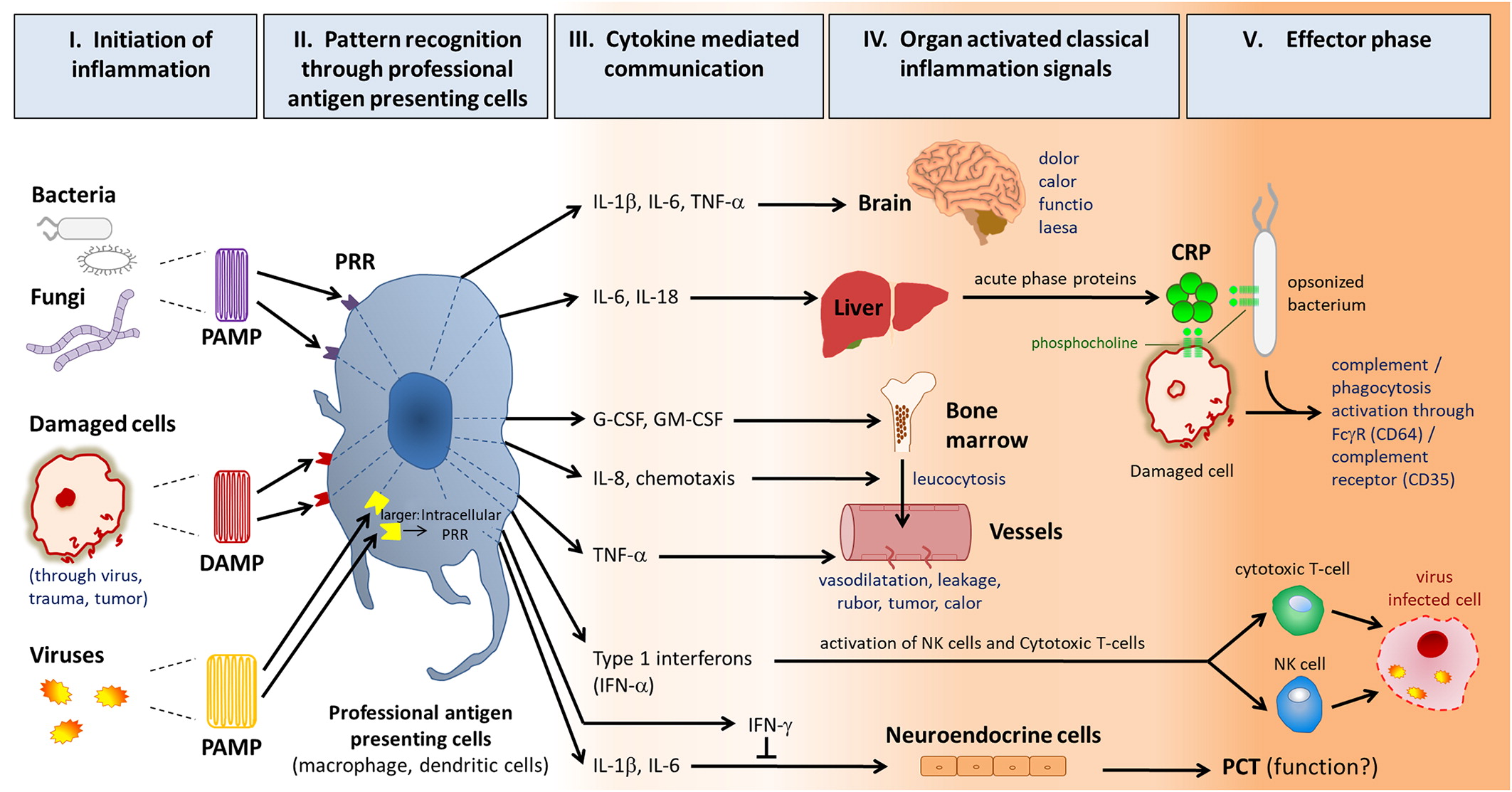
C-reactive protein and other biomarkers—the sense and non-sense of using inflammation biomarkers for the diagnosis of severe bacterial infection

Diagnostic markers of acute infections in infants aged 1 week to 3 months: a retrospective cohort study | BMJ Open

A diagnostic platform for rapid, simultaneous quantification of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in human serum - eBioMedicine
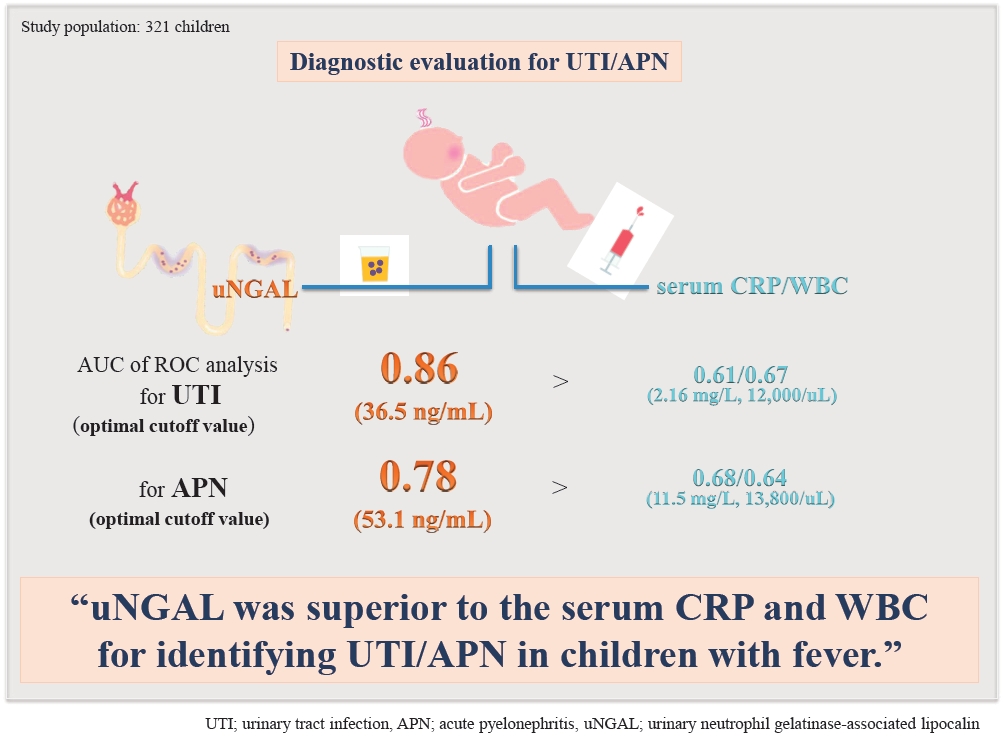
Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a marker of urinary tract infection among febrile children

Clinical application of low erythrocyte sedimentation rate/high C‐reactive protein to antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody‐associated vasculitis - Park - 2022 - Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis - Wiley Online Library
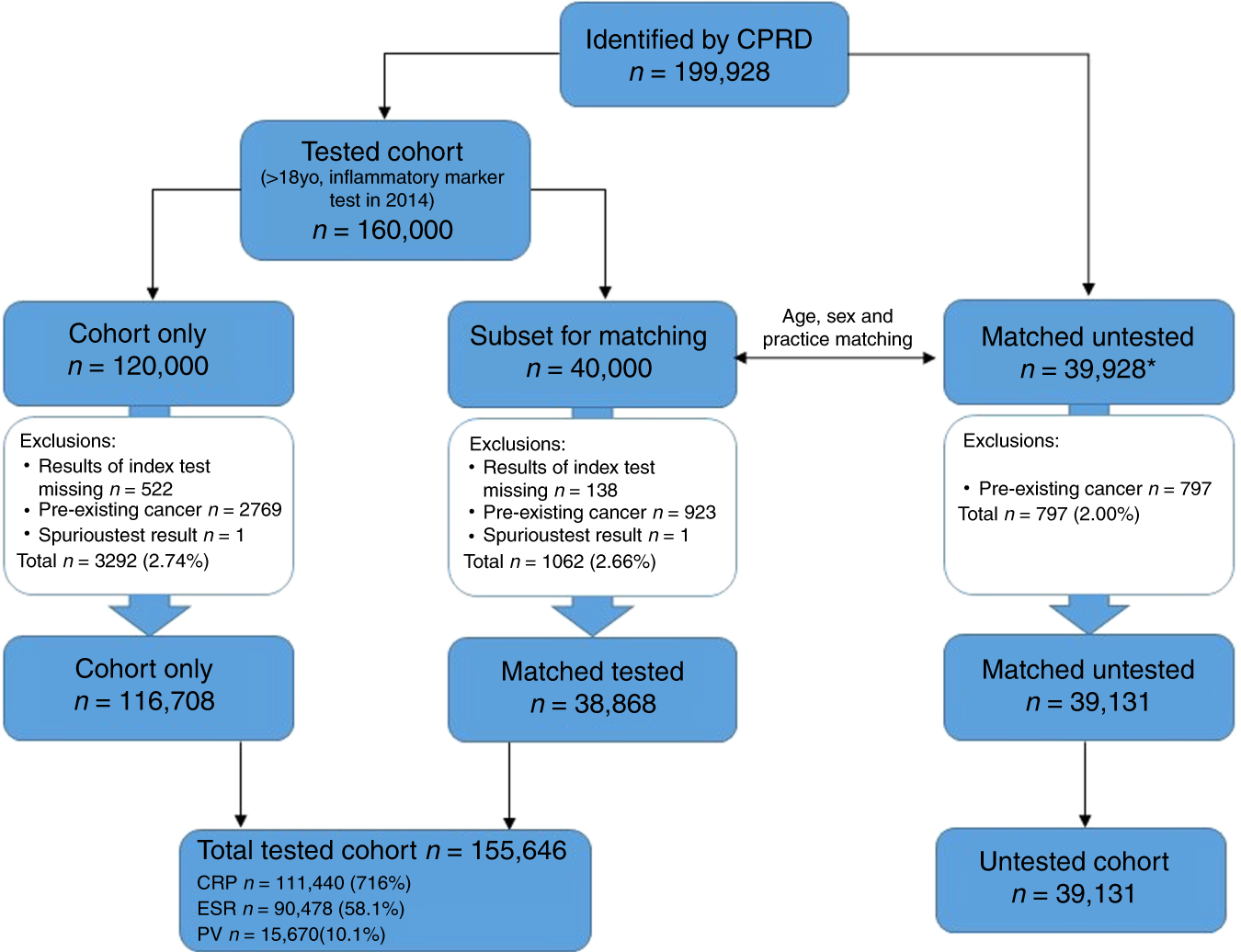
Predictive value of inflammatory markers for cancer diagnosis in primary care: a prospective cohort study using electronic health records | British Journal of Cancer

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/188021_color3-5be479cdc9e77c0051389c14.png)